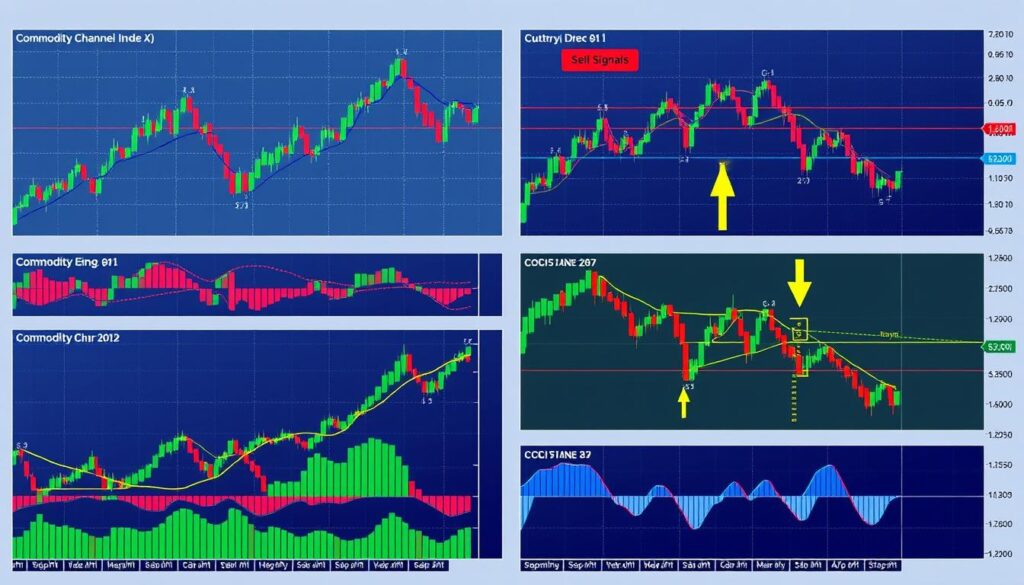
The Commodity Channel Index (CCI) is a versatile momentum oscillator created by Donald Lambert in the 1980s. It helps traders identify cyclical trends across various asset classes, including stocks, forex, and commodities. By utilizing the CCI in technical analysis, traders can gain valuable insights into market trends and make more informed decisions. The CCI is a powerful tool for CCI trading, allowing traders to identify overbought and oversold conditions, as well as potential market reversals.
Understanding the Commodity Channel Index is essential for any trader looking to improve their technical analysis skills. The CCI measures the deviation of a security’s price from its average over a specified period, providing traders with a clear picture of market trends. By combining the CCI with other technical indicators, traders can develop a comprehensive trading strategy that incorporates CCI trading principles.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- The Commodity Channel Index (CCI) is a momentum oscillator used to identify cyclical trends in commodities, stocks, and forex.
- The CCI is a valuable tool for technical analysis, helping traders identify overbought and oversold conditions.
- CCI trading involves using the indicator to identify potential market reversals and trend changes.
- The CCI can be combined with other technical indicators, such as moving averages and Bollinger Bands, to develop a comprehensive trading strategy.
- Understanding the CCI is essential for traders looking to improve their technical analysis skills and make more informed trading decisions.
- The CCI can be applied to various timeframes, including day trading and swing trading, to identify strong trends and entry points.
Understanding the Commodity Channel Index (CCI)
The Commodity Channel Index, or CCI, is a momentum oscillator that helps traders identify potential reversals and trend strength. Introduced by Donald Lambert in 1980, the CCI was initially designed to identify cyclical trends in commodity prices. Over time, it has gained popularity across various financial markets, becoming a versatile tool for traders.
The CCI definition is rooted in its ability to measure the difference between the current price and the historical average price. This is calculated using the formula CCI = (Typical Price – Moving Average) / (0.015 x Mean Deviation). Traders commonly use 20 periods to analyze the CCI, although different period lengths can affect the indicator’s volatility.
What is the CCI Indicator?
The CCI indicator is a valuable tool for traders, providing insights into trend strength and potential reversals. It can signal new trends, identify overbought or oversold levels, and detect trend weakness when diverging from price. When the CCI transitions from negative or near-zero to above 100, it may indicate the start of an uptrend. Conversely, downtrend signals occur when the CCI shifts from positive readings to below -100.
Historical Development of CCI
Donald Lambert’s innovative work in the 1980s laid the foundation for the CCI. Since its introduction, the CCI has become a widely used indicator, applied across various markets, not limited to commodities. Traders look for divergences between price and CCI movement as potential reversal indicators, making it a powerful tool for informed trading decisions.
Core Components of the CCI Formula
The CCI formula consists of several key components, including the typical price, moving average, and mean deviation. The 0.015 constant in the CCI calculation ensures that 70 to 80 percent of CCI values fall within the range of +100 to -100. This allows traders to identify overbought levels above +100 and oversold levels below -100, adjusting these levels based on the security’s volatility.
The CCI is an unbound oscillator without specific upside or downside limits, making interpretations of overbought or oversold conditions subjective. However, by understanding the CCI definition and its core components, traders can harness its power to inform their trading strategies and make more informed decisions.
The Mathematical Foundation Behind CCI Calculations
The CCI formula is a crucial component in calculating CCI values. It is calculated as CCI = (Typical Price – SMA of Typical Price) / (0.015 x Mean Deviation). Understanding this formula is essential for interpreting CCI signals and fine-tuning the indicator to suit your trading style.
The typical price is a key element in the CCI formula, representing the average of the high, low, and close prices. Calculating CCI requires determining the typical price and then using it to find the simple moving average and mean deviation.
Here is a breakdown of the steps involved in calculating CCI:
- Determine the typical price
- Calculate the simple moving average of the typical price
- Calculate the mean deviation
- Use these values to calculate the CCI
By understanding the mathematical foundation behind CCI calculations, traders can gain more confidence in using the indicator to make informed trading decisions.
| Indicator | Default Length | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Fast period CCI | 14 | Short-term trend probability |
| Middle period CCI | 25 | Confirm market mid-term uptrends |
| Slow period CCI | 50 | Confirm long-term uptrends |
Key Components of the CCI Indicator
The Commodity Channel Index (CCI) is a versatile technical analysis tool that helps traders evaluate the momentum of price trends. At its core, the CCI indicator fluctuates between -100 and +100 on a chart, with readings outside this range indicating extreme market conditions. The CCI zero line serves as a crucial reference point, separating positive and negative values.
The CCI values typically range between -100 and +100, with overbought levels usually set at +100 and oversold levels set at -100. These levels can signal potential reversals in the market. Understanding the significance of the CCI zero line and how to interpret overbought and oversold levels is essential for mastering the CCI indicator.
By recognizing the CCI zero line and overbought and oversold levels, traders can make more informed decisions about their investments. The CCI is a powerful tool for identifying trends, market saturation levels, and potential trade opportunities based on threshold levels, zero-crossing, and divergence.
Setting Up Your CCI Indicator on Trading Platforms
To start using the Commodity Channel Index (CCI) in your trading, you’ll need to set it up on your preferred trading platform. Popular platforms like MetaTrader, TradingView, ThinkorSwim, and NinjaTrader all support CCI. When setting up the CCI indicator, you can customize its appearance and adjust key settings like the lookback period. The default period setting for the CCI is commonly 14, but you can adjust this based on your individual preferences and current market conditions.
Here are the general steps to follow:
- Open your trading platform and navigate to the indicator settings.
- Search for the CCI indicator and add it to your chart.
- Adjust the lookback period and other settings as needed.
- Set up alerts for specific CCI values to ensure you never miss a trading opportunity.
By customizing your CCI settings, you can tailor the indicator to your trading style and preferences. This may involve experimenting with different period settings, such as shorter timeframes for more frequent signals or longer timeframes for more robust trends. Remember to continuously monitor and adjust your CCI settings to align with changing market conditions and optimize your trading performance.
With your CCI indicator set up and customized, you’re ready to start using it in your trading analysis. In the next section, we’ll explore how to use the CCI in trading analysis, including reading basic CCI signals, identifying market trends, and spotting divergence patterns.
How to Use the Commodity Channel Index in Trading Analysis
To effectively use the Commodity Channel Index (CCI) in trading analysis, it’s essential to understand how to read basic CCI signals, identify market trends, and spot divergence patterns. The CCI measures the current price level relative to an average price level over a given period, providing valuable insights into trend identification and potential reversals.
CCI signals are generated when the indicator moves above or below certain levels, typically +100 and -100. These levels indicate overbought and oversold conditions, respectively. By analyzing CCI signals, traders can identify potential buy or sell opportunities and confirm market trends. For instance, when the CCI moves above +100, it signals a strong uptrend, while a move below -100 indicates a strong downtrend.
In addition to reading CCI signals, traders can use the indicator to identify divergence patterns. Divergence occurs when the price movement does not align with the CCI indicator, indicating a potential weakness in the current trend. By spotting divergence patterns, traders can anticipate potential reversals and adjust their trading strategies accordingly. The key to successful trading with CCI is to combine it with other forms of analysis, such as trend identification and risk management, to maximize profits and minimize losses.
Some key points to consider when using CCI in trading analysis include:
- CCI values fluctuate above and below zero, with higher values indicating prices far above their average and lower values showing prices significantly below their average.
- The percentage of CCI values that typically fall within the +100 and -100 range depends on the number of periods used in the calculation.
- Around 70 to 80 percent of CCI values fall between +100 and -100, making buy or sell signals generate approximately 20 to 30 percent of the time.
By mastering the use of CCI signals, trend identification, and divergence patterns, traders can gain a competitive edge in the markets and make more informed trading decisions. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or just starting out, incorporating CCI into your trading strategy can help you navigate the markets with confidence and precision.
Optimal CCI Settings for Different Trading Timeframes
When it comes to using the Commodity Channel Index (CCI) in trading, one size doesn’t fit all. The default CCI period is 14, but traders often adjust this based on their trading style and timeframe. For day trading CCI, a shorter period such as 10 or 11 can be used to capture short-term market movements. On the other hand, swing trading CCI may involve a longer period, such as 20 or 21, to identify medium-term trends and reversals.
In terms of CCI timeframes, traders need to consider the optimal settings for their specific trading strategy. This may involve experimenting with different periods and settings to find what works best. Some traders may prefer a shorter period for day trading CCI, while others may prefer a longer period for swing trading CCI. Ultimately, the key is to find a setting that works for your trading style and timeframe.
- Short-term trading: 10-14 periods
- Medium-term trading: 20-21 periods
- Long-term trading: 30-50 periods
By adjusting the CCI settings to suit your trading style and timeframe, you can improve your trading results and make more informed decisions.
Advanced CCI Trading Strategies
Advanced CCI strategies involve combining the Commodity Channel Index with other indicators or techniques to create a robust trading system. By using CCI trading system in conjunction with other tools, traders can enhance their market analysis and make more informed decisions. One approach is to use multiple CCI indicators with different timeframes to confirm signals and identify trends.
Some traders also use CCI strategies that involve trading divergences, where the CCI indicator and price action are not aligned. This can be a powerful way to identify potential reversal points in the market. Additionally, advanced trading techniques such as using CCI with other indicators, like moving averages or RSI, can help traders to filter out false signals and stay focused on high-probability trades.
By mastering these CCI strategies and incorporating them into a CCI trading system, traders can take their trading to the next level and potentially improve their results. It’s essential to remember that advanced trading techniques require practice and discipline to execute effectively, so it’s crucial to backtest and refine any strategy before implementing it in live markets.
Combining CCI with Other Technical Indicators
When used alone, the Commodity Channel Index (CCI) can provide valuable insights into market trends and potential trading opportunities. However, combining CCI with other technical indicators can significantly enhance the reliability of trading signals. This approach allows traders to confirm CCI readings with other indicators, reducing the risk of false signals and improving overall trading performance.
One effective combination is using CCI and moving averages. By overlaying a moving average on the price chart, traders can identify the trend direction and potential entry points. For example, when the CCI crosses above the zero line and the price is above the moving average, it can indicate a strong uptrend. Similarly, combining CCI with the Relative Strength Index (RSI) can provide a more comprehensive view of market momentum. The RSI measures the magnitude of recent price changes, helping traders identify overbought and oversold conditions.
CCI and Volume Indicators
Another useful combination is using CCI with volume indicators. By analyzing volume data, traders can gauge the strength behind price movements. For instance, if the CCI indicates an overbought condition, but the volume is decreasing, it may suggest a potential trend reversal. The following table illustrates some common combinations of CCI with other technical indicators:
| Indicator Combination | Description |
|---|---|
| CCI and Moving Averages | Confirm trend direction and identify potential entry points |
| CCI and RSI | Provide a comprehensive view of market momentum and identify overbought/oversold conditions |
| CCI and Volume Indicators | Gauge the strength behind price movements and identify potential trend reversals |
By combining CCI with other technical indicators, traders can develop a more robust trading strategy that incorporates multiple perspectives. This approach can help traders make more informed decisions and improve their overall trading performance.
Common CCI Trading Mistakes to Avoid
When using the Commodity Channel Index (CCI) in trading, it’s essential to be aware of common CCI trading errors that can lead to poor trading outcomes. One of the most significant mistakes is over-reliance on CCI without considering other market factors, which can result in avoiding false signals and incorrect CCI interpretation mistakes.
Some common mistakes include ignoring the overall market context and using inappropriate CCI settings for the chosen timeframe. To avoid these mistakes, traders should use CCI in conjunction with other technical indicators and consider fundamental analysis and market sentiment.
By being aware of these common mistakes and taking steps to avoid them, traders can use CCI more effectively and confidently in their trading. This includes properly managing risk, setting stop-loss orders, and adapting trading strategies to changing market conditions.
| Mistake | Consequence | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Over-reliance on CCI | False signals and poor trading outcomes | Use CCI with other technical indicators and consider fundamental analysis |
| Ignoring market context | Missed trading opportunities or unfavorable trade entries | Consider overall market conditions and sentiment |
| Inappropriate CCI settings | Incorrect signals and poor trading outcomes | Adjust CCI settings according to the chosen timeframe and market conditions |
Risk Management When Trading with CCI
Effective CCI risk management involves a combination of proper position sizing, strategic stop loss placement, and a clear plan for taking profits. This approach helps protect your capital and maintain consistent profitability in your CCI trading.
To achieve this, consider the following key elements:
- Position sizing guidelines: Determine the right trade size based on your risk tolerance and CCI signals.
- Stop loss placement: Use CCI levels to set logical exit points and limit potential losses.
- Profit taking: Develop a strategy for taking profits, such as scaling out of positions or using CCI to identify potential reversal points.
By implementing these stop loss strategies and profit taking with CCI techniques, you can better manage your risk and improve your overall trading performance. Remember to continuously review and adjust your risk management approach as market conditions change.
CCI Trading in Different Market Conditions
When it comes to using the Commodity Channel Index (CCI) in trading, it’s essential to understand how to adapt to different market conditions. The CCI can be used effectively in both trending and sideways markets, but the interpretation of signals may differ depending on the market condition. In trending markets, traders might consider buying when the CCI is above +100 and selling when it is below -100.
The CCI is particularly useful in market condition analysis, as it helps traders identify overbought and oversold conditions. In CCI in trends, the indicator can signal potential trend reversals, while in CCI in ranging markets, it can help identify mean reversion trades. By mastering these techniques, traders can apply the CCI successfully across various market conditions.
Some key points to consider when using the CCI in different market conditions include:
- Identifying overbought and oversold conditions
- Spotting trend reversals
- Using the CCI in conjunction with other technical analysis tools
By understanding how to use the CCI in different market conditions, traders can enhance their versatility and improve their trading results. Whether trading in trending or sideways markets, the CCI can be a valuable tool in market condition analysis.
Real-World CCI Trading Examples
CCI case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of the Commodity Channel Index in various trading scenarios. By examining practical CCI application, traders can gain valuable insights into how the indicator performs in real-world markets. For instance, CCI trade examples can show how the indicator identifies overbought and oversold conditions, providing opportunities for traders to enter or exit positions.
A key aspect of using the CCI is understanding its signals and how they relate to market conditions. Practical experience with the indicator is essential for developing a trading strategy that incorporates CCI trade examples. By analyzing CCI case studies, traders can refine their approach and improve their trading decisions.
Some notable CCI trade examples include:
- Identifying trend reversals using divergence
- Confirming trend continuation with CCI signals
- Using CCI to set stop-loss levels and limit potential losses
These examples illustrate the versatility of the CCI and its potential to enhance trading performance. By studying CCI case studies and applying practical CCI application, traders can develop a deeper understanding of the indicator and its role in their trading strategy.
| CCI Signal | Market Condition | Trading Decision |
|---|---|---|
| Overbought | Bullish trend | Sell or short |
| Oversold | Bearish trend | Buy or cover |
Backtesting Your CCI Strategy
To refine your trading approach, CCI backtesting is essential. This process involves applying your strategy to historical data to evaluate its effectiveness. By doing so, you can identify potential flaws and areas for improvement, ultimately enhancing your trading performance analysis.
A key aspect of strategy optimization is creating a robust testing framework. This framework should include a thorough analysis of your CCI strategy’s performance across various market conditions and timeframes. You can use historical data to simulate trades and assess the strategy’s profitability.
- Lookback periods: Short lookback periods, such as 5-9 days, can help identify overbought and oversold conditions.
- Thresholds: Establishing optimal buy and sell thresholds, such as -90 and +100, can improve your strategy’s performance.
- Market conditions: Test your strategy in different market environments, including trending and sideways markets.
By conducting thorough CCI backtesting and strategy optimization, you can refine your approach and improve your trading performance analysis. This, in turn, can help you make more informed trading decisions and increase your chances of success in the markets.
Developing Your Personal CCI Trading Plan
A well-defined CCI trading plan is essential for achieving success in the markets. This plan should include entry and exit rules, risk management guidelines, and clear objectives based on your personal trading style and trading goals. To develop a comprehensive CCI trading plan, you need to consider your risk tolerance, market analysis, and personalized strategy.
When creating your plan, consider the following key elements:
- Define clear entry and exit rules based on CCI signals
- Integrate risk management techniques, such as stop-loss and take-profit targets
- Set realistic performance objectives based on your trading goals
By following these steps and incorporating the CCI trading plan into your overall personalized strategy, you can increase your chances of success in the markets. Remember to stay disciplined and adapt your plan as needed to changing market conditions.
Customizing CCI for Different Asset Classes
When it comes to using the Commodity Channel Index (CCI) in trading, customization is key. Whether you’re trading CCI in forex, CCI for stocks, or CCI in commodities, understanding how to adapt the CCI to each market is crucial. The CCI formula, developed by Donald R. Lambert, provides a normalized view of price action, making it easier to compare different securities and timeframes.
To customize CCI for different asset classes, consider the following factors:
- Optimal period for CCI readings
- Overbought and oversold levels based on the asset being traded
- Backtesting frameworks to evaluate strategy effectiveness
For example, when using CCI in forex, you may want to adjust the period to capture the 24-hour market fluctuations. In contrast, CCI for stocks may require a different approach, taking into account the specific company or sector trends. CCI in commodities trading, on the other hand, may involve considering factors like seasonality and supply-demand dynamics.
By customizing the CCI for each asset class, traders can expand their trading opportunities and potentially improve their results. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or just starting out, understanding how to adapt the CCI to different markets can give you a significant edge in the trading world.
| Asset Class | CCI Customization |
|---|---|
| Forex | Adjust period for 24-hour market |
| Stocks | Consider company or sector trends |
| Commodities | Account for seasonality and supply-demand dynamics |
Conclusion
As your journey with the Commodity Channel Index (CCI) comes to a close, remember that the true mastery of this technical analysis tool is an ongoing process. Successful trading with CCI requires not just understanding the basics, but a commitment to continuous learning and adaptation.
Keep refining your CCI trading strategies, experimenting with different settings and combinations with other indicators like the Stochastic RSI. Regularly review your past trades, analyze what worked well and where you can improve. Staying curious and open to new insights will help you become a more versatile CCI trading professional and enhance your technical analysis skills.
Remember, the markets are ever-evolving, and your approach must evolve with them. Regularly review your CCI trading plan and be prepared to make adjustments as needed. Stay disciplined in your risk management, and never stop seeking opportunities to learn and grow. With this mindset, you’ll be well on your way to CCI trading mastery and sustainable success in the markets.
FAQ
What is the Commodity Channel Index (CCI)?
The Commodity Channel Index (CCI) is a versatile momentum oscillator that helps traders identify potential reversals and gauge trend strength in the market.
How was the CCI developed?
The CCI was originally created by Donald Lambert in the 1980s and was initially designed for commodity trading, but it has since become a widely used technical indicator across various asset classes.
What are the core components of the CCI formula?
The CCI formula involves calculating the typical price, a simple moving average, and the mean deviation to derive the CCI value.
What is the significance of the CCI’s zero line?
The zero line in the CCI represents the average or “normal” market conditions. Crossing above or below the zero line can signal potential trend changes or momentum shifts.
How can I set up the CCI indicator on my trading platform?
You can easily add the CCI indicator to your charts on popular trading platforms like MetaTrader, TradingView, and others. The process typically involves selecting the CCI from the available indicators and customizing the settings to your preferences.
How can I use the CCI in my trading analysis?
The CCI can be used to identify basic buy and sell signals, confirm market trends, and spot potential divergences between the CCI and price action, which can signal upcoming reversals.
How do I optimize CCI settings for different trading timeframes?
The ideal CCI settings can vary based on your trading timeframe. For day trading, shorter lookback periods may be more effective, while swing traders and long-term investors may benefit from adjusting the CCI parameters to suit their respective strategies.
What are some advanced CCI trading strategies?
Advanced CCI trading strategies may involve using multiple CCI indicators with different timeframes, combining CCI with other technical indicators, and leveraging CCI divergences for high-probability trades.
How can I use the CCI in combination with other technical indicators?
Pairing the CCI with indicators like moving averages, the Relative Strength Index (RSI), and volume indicators can provide a more comprehensive view of market momentum and help confirm trading signals.
What are the common mistakes to avoid when using the CCI?
Some common CCI trading mistakes include over-relying on the indicator without considering other market factors, using inappropriate CCI settings, and failing to differentiate between genuine signals and false alarms.
How can I effectively manage risk when trading with the CCI?
Proper risk management when using the CCI involves guidelines for position sizing, setting stop-loss levels, and implementing profit-taking strategies to preserve your capital and maintain consistent profitability.
How can I use the CCI in different market conditions?
The CCI can be applied effectively in both trending and sideways markets. In trending markets, you can use the CCI to identify pullbacks and potential entry points, while in ranging markets, the CCI can help identify overbought and oversold conditions for mean reversion trades.
How can I backtest my CCI trading strategy?
Backtesting your CCI strategy involves setting up a robust testing framework, collecting and preparing historical data, running tests across different market conditions and timeframes, and analyzing the results to optimize your trading approach.
How can I customize the CCI for different asset classes?
Adapting the CCI to various asset classes, such as forex, stocks, and commodities, may require adjusting the indicator’s settings and considering market-specific factors like liquidity, volatility, and seasonality.